Hand therapy ball exercises are an affordable way to increase strength and dexterity in your hands. They are simple to use and extremely versatile, which makes it easy to practice a wide range of effective exercises to strengthen the hands.
Below, we review 8 hand therapy ball exercises to improve fine motor skills after stroke.
Effective Hand Therapy Ball Exercises
The most effective way to promote hand recovery after stroke is through high-repetition practice. Consistently practicing these 8 hand therapy ball exercises will help stimulate the brain and promote its ability to rewire itself through neuroplasticity.
Start with a set of 10 repetitions of each exercise, then build up your strength to aim for 2-3 sets of 10. As long as these exercises do not cause you pain, you can do them a few times a day!
1. Power Grip

This hand therapy ball exercise will strengthen your grip to improve grasp and release of objects. Grasping the ball will develop the flexor muscles in your forearm.
It will also be important to practice releasing the ball, which will strengthen the extensor muscles on the outside of your forearm. This exercise can also help relieve joint pain, stress, and anxiety.
Squeeze the therapy ball with your fingers and thumb, as if making a fist. Squeeze, then release the ball completely, opening your fingers as wide as you can.
2. Pinch
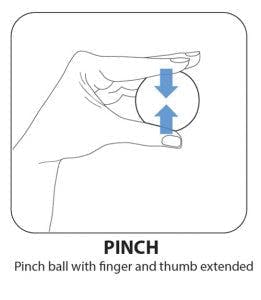
Pinch the hand therapy ball with your fingers and thumb extended. By extended, we mean to keep all the knuckles in your fingers straight. This will help strengthen muscles different from the ones used when your fingers are curled (as in the first exercise).
To make this hand therapy ball exercise more challenging, pinch the ball for a longer period of time.
3. Thumb Flexion & Extension
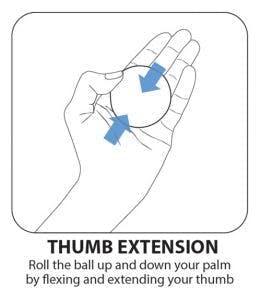
The thumb plays an essential role in various hand functions including pinching and grasping, so it’s imperative to strengthen its muscles to improve control.
With your palm as flat as possible, place the therapy ball on your palm and use your thumb to keep it in place. Then, use your thumb to roll the ball up and down your palm. This movement is more challenging and requires only specific thumb muscles.
4. Table Roll
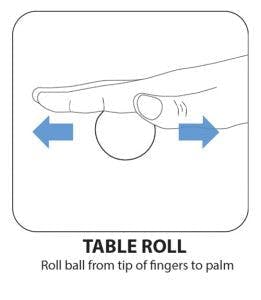
Place the hand therapy ball on a table with your hand on top of it. Then, while keeping a flat hand, roll the ball from the base of your palm up to your fingertips.
Placing too much pressure on the ball will make it difficult to maneuver. This hand therapy ball exercise will help individuals practice stabilizing their arm and hand so that only a specific amount of pressure is on the ball.
5. Finger Flexion
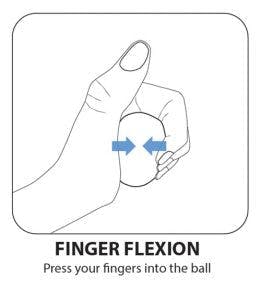
Unlike the Power Grip exercise, you squeeze the ball without the use of your thumb. Hold the therapy ball in your palm by pressing it with your fingers. Press and release.
Notice how much more challenging it is to squeeze the ball without using your thumb. This will help strengthen the muscles that allow you to bend your fingers.
6. Thumb Roll
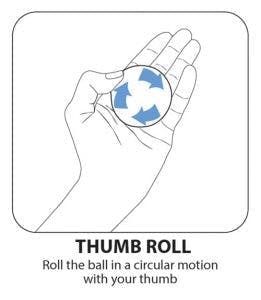
This hand therapy exercise isolates your thumb and encourages you to move it through its entire range of motion. As a result, it will help prevent stiffness and improve control.
Place the therapy ball on your palm. Keep your palm as flat as possible and use your thumb to keep it in place. Then, use your thumb to roll the ball in a circle on your palm.
7. Finger Squeeze
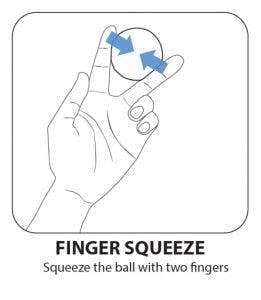
This hand therapy ball exercise will help individuals strengthen their finger adduction muscles. These muscles allow you to bring the fingers together, which is needed to grasp objects.
Place the therapy ball between two fingers and squeeze your fingers together. Squeeze and release. You can do this with any combination between the fingers, so you are sure to exercise all your fingers!
Some fingers will be more difficult than others (like your ring and pinky finger), but your effort still has an effect on your nervous system, so don’t worry if you see little movement.
8. Thumb Opposition
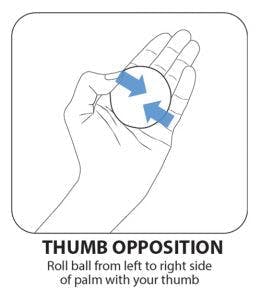
This therapy ball exercise is similar to the Thumb Roll, but you will roll the ball side-to-side instead of in circles. Start by placing the therapy ball on your palm and using your thumb to keep it in place. Then, use your thumb to move the ball from left to right.
Benefits of Hand Therapy Ball Exercises
It’s important to tailor your hand therapy exercises to suit your recovery goals. Some hand therapy balls have more resistance than others. Choose ones that suit your goals. Some individuals may need to strengthen their hands, while others might use these exercises to regain mobility in their hands.
When neurological injury is involved, the focus should not be placed solely on trying to increase resistance. Instead, the focus should be placed on repetition, which provides the brain with the stimulation it needs to rewire itself.
Cater your hand therapy exercise regimen to suit your goals. You may even like adding some therapy putty exercises too! Happy exercising!
The post Hand Therapy Ball Exercises to Improve Fine Motor Skills appeared first on Flint Rehab.



