Coup-contrecoup brain injuries occur when a head injury results in damage to 2 sides of the brain (the side of the trauma and the opposite side of the brain). Because they affect multiple areas of the brain, these head injuries can result in various secondary complications and are one of the most serious types of traumatic brain injury.
To help you understand what recovery from a coup-contrecoup brain injury entails, this article will discuss:
- What Causes a Coup-Contrecoup Brain Injury?
- Diagnosing a Coup-Contrecoup Injury
- Coup-Contrecoup Injury Symptoms and Signs
- Coup-Contrecoup Brain Injury Treatment
What Causes a Coup-Contrecoup Brain Injury?
The terms coup and contrecoup are French for “blow” and “counterblow.” Therefore, a coup-contrecoup injury actually refers to two separate brain injuries sustained during the same incident.
A coup injury refers to the brain damage that occurs directly under the point of impact. In contrast, a contrecoup injury occurs on the opposite side of the brain from where the head is struck. These injuries can occur separately (as only a coup injury or only a contrecoup injury), but if the blow is strong enough, they often appear together (as a coup-contrecoup injury).
The brain is encased within the skull and is surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid. Generally, this provides enough protection from the bumps and jolts we experience throughout the day. However, when the force of a blow to the head is severe enough, the brain can slam against the skull, causing serious damage.
Most coup-contrecoup injuries occur when the person’s head slams against a stationary object. For example, if a car hits you from behind, you may experience whiplash and hit your head against the steering wheel.
When the skull hits the object, the brain moves toward the object until it collides with the skull. Then, due to the impact of the initial trauma, it rebounds, causing the second impact to the brain due to hitting the opposite side of the skull. This is demonstrated in the video below.
Coup-contrecoup injuries are considered focal brain injuries, meaning that they are confined to specific areas of the brain. While individuals may demonstrate symptoms associated with both areas of brain damage, the contrecoup injury is often more severe than the coup injury. In the following section, we’ll discuss the various signs and symptoms an individual may experience after this type of head and brain injury.
Diagnosing a Coup-Contrecoup Injury
Diagnosis of a coup-contrecoup injury usually involves a physical and neurological examination. Doctors are able to identify whether a coup, contrecoup, or coup-contrecoup injury has occurred through a detailed assessment, along with imaging tests such as an MRI or CT scan. If imaging tests reveal two distinct areas of damage that occur opposite from one another, it is usually considered a coup-contrecoup injury.
Coup-contrecoup injuries often involve brain contusions (bruising) and/or intracerebral hemorrhages (bleeding). Although individuals may display a wide variety of symptoms depending on which areas of the brain sustained damage, imaging tests can often paint a clearer picture in order to obtain an accurate diagnosis.
Coup-Contrecoup Injury Symptoms
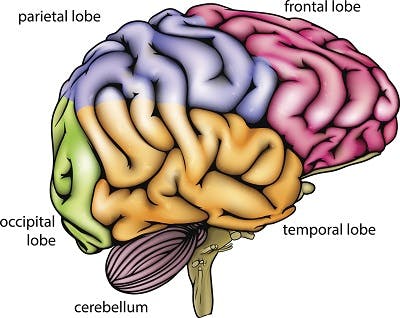
Coup-contrecoup brain injuries may affect any 2 regions of the brain, with one injury at the point of impact and the other at the opposite part of the brain. While symptoms may vary depending on which areas of the brain sustain damage, the most common symptoms of coup-contrecoup injuries include confusion and seizures.
Each hemisphere of the brain is divided into 4 lobes: the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, and temporal lobe. Most brain functions involve the collaboration of various regions of the brain. However, generally there is a specific region that each function can be primarily attributed to (the region that plays the greatest role in regulating that function).
Although coup-contrecoup injuries can affect any 2 areas of the brain, the frontal and temporal lobes are most often affected. Below, we’ll discuss common signs and symptoms of damage to each lobe of the brain.
1. Frontal Lobe Damage
The frontal lobe takes up the largest area of the cerebral cortex. It is primarily responsible for higher cognitive skills, such as attention, planning, memory, and behavior.
A coup-contrecoup injury that damages the frontal lobe may result in the following functional challenges:
- Impulsivity
- Poor judgement
- Memory loss
- Concentration problems
- Aphasia (language difficulties)
- Behavioral and personality changes
- Problem-solving difficulties
- Decision-making problems
Additionally, damage to the frontal lobe may impair motor control. As a result, individuals may experience weakness or paralysis of voluntary muscle movements.
2. Parietal Lobe Damage
The parietal lobe is located behind the frontal lobe. This region of the brain is responsible for processing sensory information such as touch and proprioception (your sense of where your body is in space). If a coup-contrecoup injury affects the parietal lobe, it may cause problems with sensation and perception. As a result, individuals may struggle to interact with their surroundings.
Common symptoms of parietal lobe damage include:
- Numbness
- Burning
- Poor hand-eye coordination
- Difficulty differentiating right from left
- Loss of direction
- Difficulties distinguishing temperatures
- Abnormal perception of pain
- Difficulties with reading, writing, and mathematics
3. Occipital Lobe Damage
Behind the parietal lobe and towards the back of the brain resides the occipital lobe. This region of the brain is primarily responsible for processing visual stimuli.
A coup-contrecoup injury that affects the occipital lobe may involve different types of blindness and visual distortions, such as:
- Partial blindness (hemianopsia, also known as a visual field cut)
- Decreased peripheral vision
- Visual hallucinations/illusions
- Word blindness (alexia)
- Poor visual recognition and attention
4. Temporal Lobe Damage
The temporal lobe is located in the lower middle part of the brain, next to your temples and above the ears. Its main responsibility is processing auditory information, but it also plays a role in interpreting smell and sight.
A coup-contrecoup injury that affects the temporal lobe may result in:
- Hearing loss
- Trouble recognizing faces and objects
- Memory loss
- Difficulties understanding spoken language
- Difficulties finding the right words to say
- Attention problems
- Changes in emotional behavior
5. Additional Signs and Symptoms
Because coup-contrecoup brain injuries may affect any region of the brain, individuals may also experience other common secondary effects of brain injury, including:
- Severe headache
- Seizures
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Emotional challenges
- Sensitivity to sound and light
- Amnesia (memory loss)
- Nausea
- Slurred speech
Now that you understand the potential outcomes the following section will discuss how to treat this type of head and brain injury.
Coup-Contrecoup Brain Injury Treatment
Treatment of coup-contrecoup injuries primarily depends on the severity of the injuries and which regions of the brain are affected. Every injury is unique, so a personalized approach to treatment that targets each individual’s specific secondary effects is ideal.
Frequently recommended rehabilitative interventions include:
- Physical therapy. If motor control and/or balance is affected after a injury, physical therapy can help improve these functions through targeted exercises.
- Occupational therapy. Occupational therapy can help individuals become as functional and independent as possible by rehabilitating affected functions and/or teaching survivors new ways to perform everyday activities.
- Speech therapy. If your injury results in aphasia, you may lose your ability to communicate. A speech therapist can help you regain language skills, as well as relearn swallowing skills if needed.
- Cognitive training. Cognitive training may help improve memory, attention, problem-solving, and learning skills after injury.
To improve outcomes after a coup-contrecoup injury, it is essential to practice rehabilitative exercises and activities as much as possible. This will stimulate the brain, reinforce demand for those functions, and promote neuroplasticity (the brain’s ability to rewire itself).
One way to perform as many repetitions as possible is to download a neurorehabilitation app on your phone or tablet, such as the CT Speech & Cognitive Therapy App. It provides access to over 100,000 speech and cognitive therapy exercises designed by speech therapists so you can practice whenever you want.
Additionally, the CT App targets a variety of functions including listening, speaking, attention, memory, and visual processing. This makes it ideal for all coup-contrecoup injury survivors, regardless of which regions of the brain are affected.

Likewise, if a coup-contrecoup injury has affected your mobility, it may be worth investing in home rehab devices like the Award Winning FitMi Home Therapy to retrain the brain to move again. FitMi includes 40 exercises for the leg, core, arm, and hand. They’re all designed by physical and occupational therapists to strengthen and improve motor control over muscles affected by brain injury.
Here’s what a caregiver said about FitMi during her son’s brain injury recovery:
“My son Sam has a TBI as a result of being hit by a car 5 years ago. We were looking for some way to get him to move since he would prefer to sit on the couch all day. He works with the FitMi on his own without anyone telling him to, and that is saying a lot. Any moving he does is good for him, and the FitMi is geared for reps of movements to help him continue to regain mobility. Best investment we have made since he left rehab!” — Ann L.
FitMi works best when used daily at home between outpatient therapy sessions. It helps fill in the gap when you can’t see your therapist daily or when insurance stops covering the sessions you need to continue improving.
Coup-Contrecoup Brain Injuries: Key Points
Coup-contrecoup brain injuries affect both the site of impact and the opposite side of the brain. Because two regions of the brain are affected, individuals with these injuries may experience a wide range of secondary effects. Treatment will vary depending on which regions of the brain are affected and their subsequent effects.
We hope this article helped you understand the implications of a coup-contrecoup brain injury as well as the best practices for recovering from one.
The post Coup-Contrecoup Brain Injury: Looking at Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment for this 2 Sided Head Injury appeared first on Flint Rehab.



